🐜本の進捗(優先度付きキューとUnionFind木)::9/13
いままでまともにアルゴリズムの勉強をしてこなかったので得るものが大きいです.
2-4 データ構造
二分木
すべてのノードの子の数が2以下の木
プライオリティキュー
数の追加と最小値の取り出しが行えるデータ構造を指す
二分木ヒープ
プライオリティキューを二分木を用いて実装したもの
子の数字>親の数字を満たす二分木で更新と削除のたびに左記条件を満たすまで交換を繰り返す.
実装方法
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define REP(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) template <typename T> class Heap { public: int sz = 0; T array[100001]; Heap() { } void push(T x) { int i = sz++; while (i > 0) { int p = (i - 1) / 2; if (array[p] <= x) break; array[i] = array[p]; i = p; } array[i] = x; } T pop() { T ret = array[0]; T x = array[--sz]; int i = 0; while (i * 2 + 1 < sz) { int a = i * 2 + 1, b = i * 2 + 2; if (b < sz && array[b] < array[a]) a = b; if (array[a] >= x) break; array[i] = array[a]; i = a; } array[i] = x; return ret; } }; int main(void) { Heap<float> heap; heap.push(1.6); heap.push(7.9); heap.push(-44.1); heap.push(842.0); heap.push(0.0); REP(i, 5) { cout << heap.pop() << endl; /* -44.1 0 1.6 7.9 842 */ } return 0; }
二分木なので親ノードのインデックスは(i-2)/2で取得でき,子ノードはi*2+1, i*2+2で取得が可能であることに注意しよう!!!!
$\text{function}~~push(Num: x) \rightarrow Nil$
- $arr = Array.new();sz = 0;//initialize$
- $i = sz++; // i \leftarrow \text{Self Node Index}$
- $\text{while}(i > 0):$
- $p = (i-1)/2; // p \leftarrow \text{Parent Node Index}$
- $\text{if}(arr[p] \leq x) \text{~then~~break;}$//逆転していたら抜ける
- $arr[i]=arr[p];~i=p;$
- $arr[i]=x$
$\text{function}~pop() \rightarrow Num$
- $retval = arr[0];$//返り値(最小値)
- $x = arr[-1];$//根に持ってくる値
- $i=0;$
- $\text{while}(i*2+1<sz):$//子ノードが存在する
- $l=i\times2+1,r=i\times2+2;$
- $\text{if}(r<sz$ $and$ $arr[b]<arr[a])\text{then}$ $a\leftarrow b;$
- $\text{if}(arr[a] \geq x)\text{thenbreak;}$
- $arr[i]=arr[a];~i=a;$
- $arr[i]=x;$
- $\text{return}~~retval;$
c++ のSTLにもプライオリティキューはある.そのため,イチから自分で実装するという機会はほぼないが,STLの方は最大値から取り出されるので注意が必要.
DS-1(POJ 2431)
壊れた燃料タンクを直すために距離が $L$ だけ離れている街へ向かう. タンクには最初 $P$ だけ燃料があるが,単位距離進む毎に1単位分の燃料を失う. 街までの道には $N$ 個の燃料補給所がある. $i$ 番目の補給所は故障地点から $A_i$ の位置にあり,そこで $B_i$ の燃料を補給することができる. タンクに保存できる燃料の量に上限は無い. 街まで進むために必要な最小の燃料補給の回数を答えよ. ただし,どのように進んでも街まで辿り着けない場合は $-1$ と出力せよ.
(POJ本家は街からの距離を$A_i$としていたが,蟻本では簡単のため故障地点からの位置に変えてある.)
ガソリンスタンドに寄って補給するのではなく,ガソリンスタンドに寄ったらそのガソリンスタンドで燃料を補給する権利を手に入れると考える.
つまり,通過したガソリンスタンドの補給量をPQに記憶し,燃料が尽きた地点で,立ち寄ったガソリンスタンドの中で最も補給量が大きいものを選べば良いことがわかる.
#include <queue> #include <iostream> using namespace std; #define REP(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) int main() { int N, L, P; int A[10001], B[10001]; cin >> N; REP(i, N) { cin >> A[i]] >> B[i]; } cin >> L >> P; A[N] = L; B[N] = 0; N++; priority_queue<int> pq; int ans = 0, pos = 0, tank = P; REP(i, N) { int d = A[i] - pos; while (tank - d < 0) { if (pq.empty()) { cout << "-1" << endl; return 0; } tank += pq.top(); pq.pop(); ans++; } tank -= d; pos = A[i]; pq.push(B[i]); } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }
Union-Find木
グループ分けを管理するデータ構造の一種.次のことが効率的に行える.
- 要素$a$と要素$b$が同じグループに属するかを調べる
- 要素$a$と要素$b$のグループを併合する.分割は出来ない
一つの木を一つのグループとして扱う.
併合
木同士の根に辺を張ることで,グループを併合することができる.
要素判定
根が同じ要素同士は同一グループとみなすことができる.
実装上の注意
木構造を扱うので,深さに偏りが発生すると計算量が増大してしまう.そこで,各木の深さを記憶してとき,深さの浅い木を深い方に辺を張ることで偏りの少ない木とすることができる.
また,各ノードが根を辿った場合,辺を直接根に張り直すことで根からの深さを抑えることができる.
実装例
http://www.prefield.com/algorithm/container/union_find.html
class UnionFind{ private: vector<int> arr; public: UnionFind(int size): arr(size, -1){} int root(int node){ return arr[node] < 0 ? node : arr[node] = root(arr[node]); } int size(int x){ return -arr[root(x)]; } bool unionSet(int x, int y){ x = root(x); y = root(y); if(x!=y){ if(arr[x] < arr[y]) swap(x, y); arr[x] += arr[y]; arr[y] = x; } return x != y; } bool findSet(int x, int y){ return root(x) == root(y); } };
DS-2(POJ 1182)
$N$匹の動物に対し$1..N$の番号が振られており,各々の動物は3つの$A,B,C$に 分けられる.このグルーピングには以下のような強弱関係がある.$A\rightarrow B \rightarrow C \rightarrow A$.
次の2種類の情報が$k$個与えられる.
- $x$と$y$は同じ種類である
- $x$は$y$を捕食する
入力を逐次処理した際,矛盾する記述は何個あるか.ただし矛盾した記述は以降捨てると考える.
int main(void) { bool debug = true; int N, k; int T[50001], X[50001], Y[50001]; cin >> N >> k; REP(i, k) { scanf("%d %d %d", &T[i], &X[i], &Y[i]); } UnionFind uf = UnionFind(3 * N); int ans = 0; REP(i, k){ int t = T[i]; int x = X[i] - 1; int y = Y[i] - 1; if (x < 0 || x >= N || y < 0 || y>=N){ ans++; if (debug) cout << "[*] Invalid Data (Out of length): x = " << x << ", y = " << y << endl; continue; } // Same Group if(t==1){ if(uf.findSet(x, y+N) || uf.findSet(x, y+2*N)){ ans++; if (debug){ cout << "[*] Invalid 'Same kind' input: x = "; cout << x << ", y = " << y << endl; } }else{ uf.unionSet(x, y); uf.unionSet(x + N, y + N); uf.unionSet(x + 2 * N, y + 2 * N); if (debug){ cout << "[*] Valid 'Same kind' input: x = "; cout << x << ", y = " << y << endl; } } }else if(t == 2){ // Eat Group if(uf.findSet(x, y+N) || uf.findSet(x, y+2*N)){ ans++; if (debug){ cout << "[*] Invalid 'Eat kind' input: x = "; cout << x << ", y = " << y << endl; } }else{ uf.unionSet(x, y + N); uf.unionSet(x + N, y + 2*N); uf.unionSet(x + 2 * N, y); if (debug){ cout << "[*] Valid 'Eat kind' input: x = "; cout << x << ", y = " << y << endl; } } }else{ ans++; cout << "[*] Invalid Type: t = " << t; } } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }
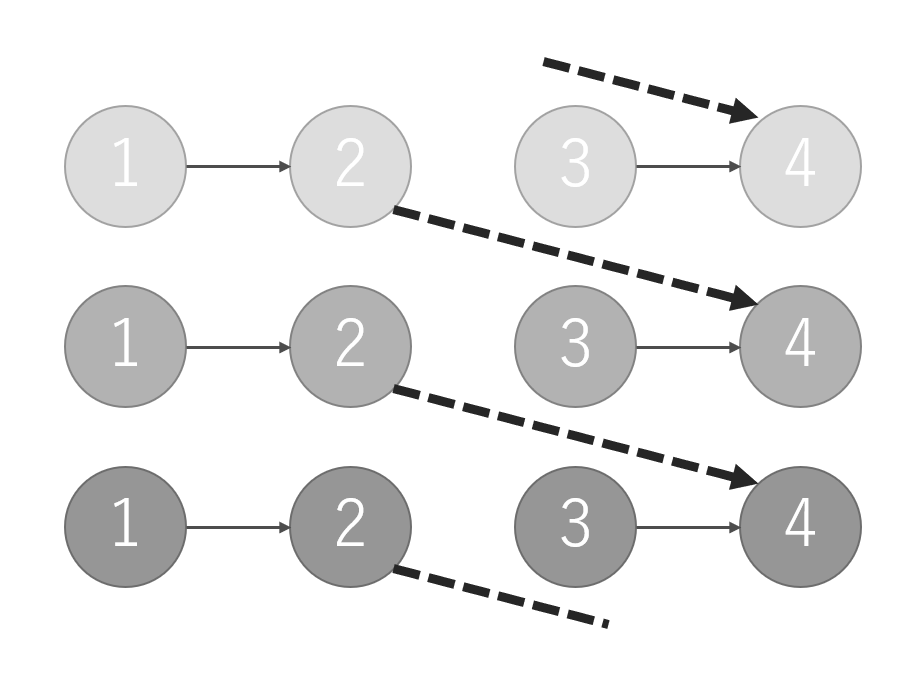
3*Nのノードを持つUnionFindを定義しておいて,$0..N-1$をグループA,$N..2N-1$をグループB,$2N..3N-1$をグループCとすることで同族ならば実線のように,捕食関係にあるならば破線のように互いを結び付けることで,各々の関係を記録することができる.